
Miosix is an OS kernel designed to run on 32bit microcontrollers, in active development since 2008.
It supports both a single process, multiple threads application model where applications are statically linked with the kernel, and an experimental multiprocess environment with memory protection that allows loading applications at runtime. The kernel is royalty-free and licensed under the GPL license with an exception that allows it to be linked with propietary application code.
Coming soon in 2025
We're working on the next release of the kernel, version 3.00, which will include several new fearures:- Fluid kernel architecture, blending an unikernel and a monolithic kernel (more information soon)
- Introducing the abstraction of processes with memory protecition on MMU-less architectures
- Multicore microcontroller support
Features
- Focus on C++ support, not just C.
- Support for the full C and C++ standard libraries, including the STL (using the newlib and libstdc++ libraries).
- Support for the standard POSIX thread API (currently threads, mutexes and condition variables).
- Effort on providing thread safe standard libraries and language features, such as C++ exception handling.
- Architecture-dependent code is separated from the kernel, making it easily portable to any 32bit microcontroller.
- Currently supports the STM32, EFM32, RP2040, ATSAM and LPC2000 micrcontroller families.
- An API separates the scheduler from the kernel, allowing to have more than one scheduler in the same codebase, and compile-time scheduler selection.
- Currently supports a priority-based scheduler, an innovative scheduler based on control theory which is the subject of academic research, and the EDF scheduler.
- FAT32 filesystem implementation, integrated with the C/C++ libraries (e.g. files can be opened with the standard fopen()).
- mxgui:
a GUI library integrated with the kernel. Provides threadsafe drawing
primitives optimized for devices with too little RAM to allow double-buffering.
Allows multiple threads to render different parts of the screen.
A pixel perfect simulator allows to test the GUI part of an application on a (Linux) PC, simplifying the process of designing an embedded user interface. An example of the capabilities of the library can be seen in this video. - mxusb: an USB device
library integrated with the kernel (e.g. allows to have threads waiting
for data on endpoints). Provides an innovative USB peripheral
autoconfiguration, based on USB descriptors.
Currently supporting STM32 microcontrollers. - Source code is well documented using Doxygen, and continuously tested by means of a testsuite distributed along with the kernel.
- Code size down to ~10KB of FLASH memory (on Cortex M3).
Getting started
For the documentation of the latest kernel have a look at the Miosix Wiki.To download the Miosix kernel, go to the download page and follow the instructions.
If you just want to have a look at the source code from a web browser, there is a Github mirror of the kernel.
In use
Skyward
Miosix is being used by Skyward in all their rockets starting from the Rocksanne I-X for on-board control and logging.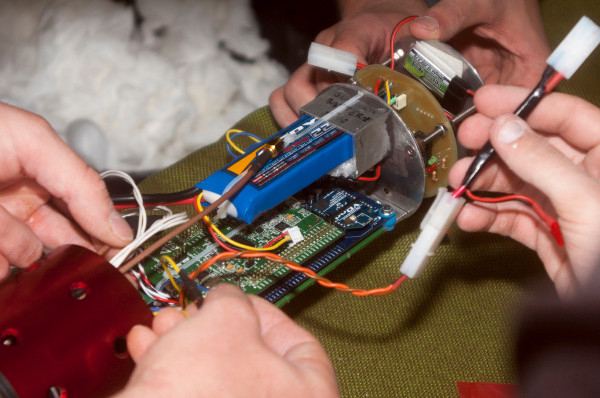
Flopsync
Miosix is used as the OS to support the FLOPSYNC-2 Wireless Sensor Network clock synchronization scheme which is currently the subject of academic research.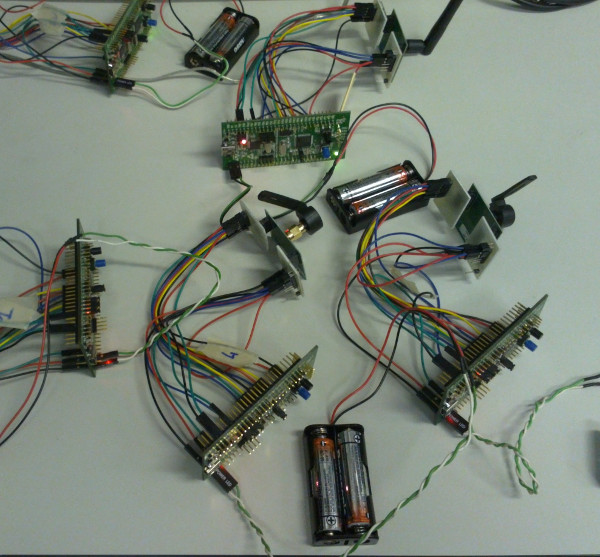
privacy policy